Interest Management [Pro]
Understanding Interest Management
When you have a game with a big world and a high player count, it becomes more and more expensive to replicate every object in the game to every connected client. It's an O(N2) problem, meaning the bandwidth sent from the server scales quadratically with the number of players connected. Interest Management mitigates this problem by filtering objects that are of no interest to the client. Usually, this is done using Area of Interest, which is the area around the player. The client will only receive objects existing in this area. Interest management is often used in battle-royale scale games
Interest Management is also useful as an anti-cheat measure. For instance, you can replicate team-specific objects to only players of the same team, using a Custom interest group, which we will learn about in this article.
Netick handles Interest Management (filters objects replicated to a client) in two phases:
- Broad Phase Filtering
- Narrow Phase Filtering
Broad Phase Filtering
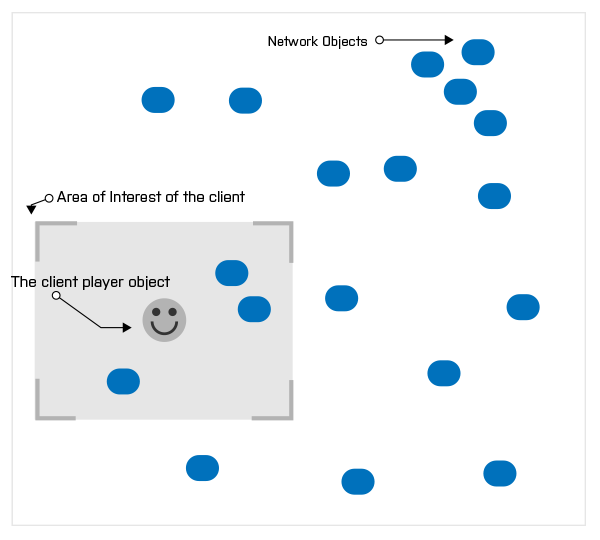
Broad Phase Filtering is done using a group. An interest management group is a list of network objects that are processed together. Every network object has an option to choose the broad phase filter source, it can be one of three options:
Global: no filtering, the object is replicated to everyone.Area of Interest: only when a client's Area of Interest intersects this object's group cell it will be replicated.Custom: using an explicitly assigned custom group through code, with an index. Only clients who explicitly choose to be interested in this group will receive updates to the object.
Note
Area of Interest implementation is done using a grid, which you can specify its settings in Netick Settings window.
Note
The number of available custom interest groups can be set in Netick Settings.
Explicitly specifying the custom interest group of an object
Object.InterestGroup = Sandbox.InterestManagement.CustomGroups[groupIndex];
Note
The above is only valid when the Broad Phase Filter of the object is set to Custom. When it's set to Area of Interest, it will only be controllable by Netick - meaning the object will be assigned a group that corresponds to its current position in the world.
Narrow Phase Filtering
Narrow Phase Filtering allows for finer control. Instead of being handled per-group basis, it's done per-object per-client basis. Which is slower. Thus, it should only be used when necessary.
Filtering an object to a specific client
Object.SetNarrowphaseInterest(client, false);
Specifying the interest of a client
Adding area of interest regions
The area of interest of the client is specified using bounding boxes that you can add.
InputSource.AddInterestBoxArea(new Bounds(transform.position, (InterestBox)));
Adding custom interest groups
InputSource.AddInterestGroup(customInterestGroupIndex);
Caution
This must be done every NetworkFixedUpdate callback since it's cleared at the end of the tick. Usually, you should do this in the movement controller of your player character.
Callbacks
There are two callbacks on NetworkBehaviour for when the interest status of an object changes in the client.
public override void OnBecameInterested()
{
// called when this client becomes interested in this object.
}
public override void OnBecameUninterested()
{
// called when this client becomes uninterested in this object.
}
One of the things you can do using these callbacks is hide/show the object when the client becomes interested/uninterested.